Assessment of blepharitis
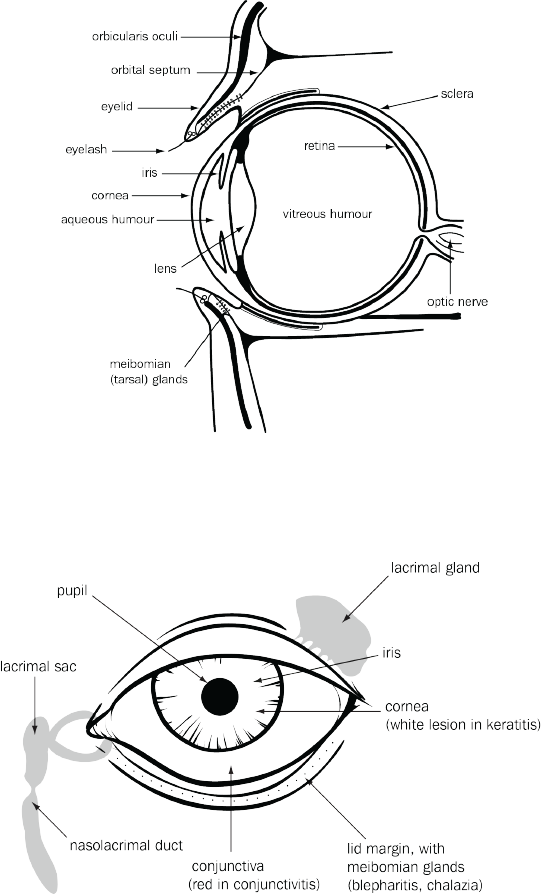
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the eyelid margins (see Diagram of the eye)The Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital (RVEEH), 2023. The pathophysiology is not fully understood, but generally involves immune-mediated damage. Blepharitis is often associated with other conditions such as seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, rosacea and dry eyes. While it can be categorised into anterior or posterior blepharitis, there is considerable overlap of symptoms, and they often co-exist.
Anterior blepharitis is an inflammation of the anterior eyelid margin involving the eyelid skin and eyelashes. It presents with symptoms of burning and grittiness in both eyes. Examination of the eyelids shows crusting, scaling and redness of the eyelid margin. Staphylococcal enzymes and toxins are thought to play a part in the pathophysiology of anterior blepharitis; in adults older than 50 years, it may be associated with Demodex mites (Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis)Shah, 2022.
Posterior blepharitis is caused by dysfunction of the meibomian glands, which are sebaceous glands at the rim of the eyelid (see Diagram of the eye) that discharge meibum with blinking. Activities that reduce blinking (eg prolonged screen time) can contribute to posterior blepharitis. Signs include redness of the eyelid margin with blocked meibomian glands and a frothy discharge along the eyelid margins (although these are difficult to see macroscopically). There may be associated chalazia.