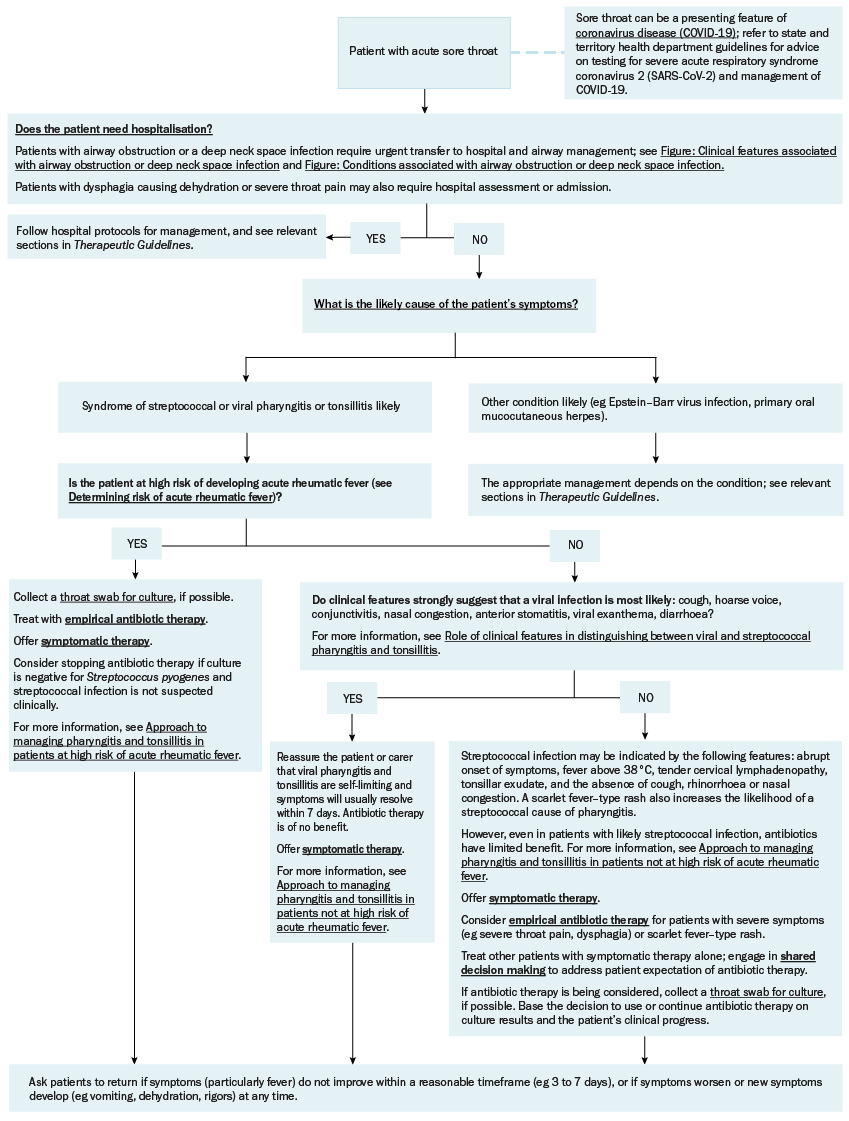
Algorithm for assessing and managing acute sore throat
Sore throat is often referred to as pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharynx) or tonsillitis (inflammation of the palatine tonsils), but it can be a symptom of many other conditions.
For an algorithm for assessing and managing acute sore throat, see here. Patient assessment is essential to ensure appropriate management. For the common syndromes of viral and streptococcal pharyngitis and tonsillitis, the approach to management depends on the patient’s risk of acute rheumatic fever—see Determining risk of acute rheumatic fever in patients with pharyngitis and tonsillitis. For the approach to managing patients at high risk of acute rheumatic fever, see here and for the approach to managing patients not at high risk of acute rheumatic fever, see here.