Treatment of mild acne
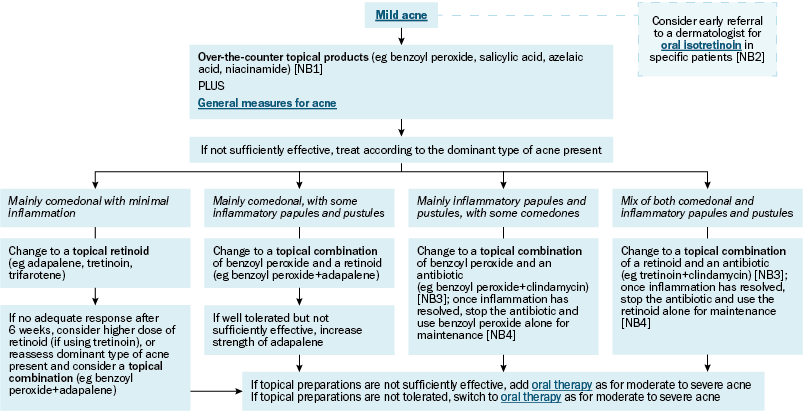
NB1: One or more over-the-counter topical products can be used for an additive effect; however, this may increase irritation.
NB2: Consider early referral if acne is scarring (even mild persistent acne can scar), presents in a patient with a family history of severe scarring acne, is resistant to other treatments, repeatedly relapses, or has a marked negative emotional and social effect.
NB3: Benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin can be irritating; topical clindamycin can be used alone if the patient’s skin is prone to irritation (eg patients with atopic skin conditions).
NB4: Avoid using topical antibiotic therapy long term. Once papular inflammation has resolved or inflammatory acne activity is controlled, change to a single-ingredient preparation containing a topical retinoid or benzoyl peroxide for maintenance. If the inflammation recurs, resume the topical combination containing an antibiotic, and regularly review for ongoing need.
Consider early referral to a dermatologist for oral isotretinoin if acne:
- is scarring (even mild persistent acne can scar)
- presents in a patient with a family history of severe scarring acne
- is resistant to other treatments, or repeatedly relapses
- has a marked negative emotional and social effect.
Mild acne is initially treated with topical products in addition to general measures. Apply the product to the whole area affected by acne, not just to single lesions.
For initial treatment of mild acne, suggest over-the-counter topical products. Benzoyl peroxide is available in 2.5%, 5% and 10% strengths. Most patients start with benzoyl peroxide 5%; however, if the patient has a history of atopic dermatitis, or dry or sensitive skin, start with benzoyl peroxide 2.5%. Benzoyl peroxide 10% is usually too irritating to use on the face. Other over-the-counter topical treatments for mild acne include salicylic acid, azelaic acid and niacinamide. One or more over-the-counter topical products can be used for an additive effect; however, this may increase irritation. For more information on over-the-counter topical products, see Treatments used for acne.
If over-the-counter topical products are not sufficiently effective, subsequent treatment depends on the dominant type of acne present (eg comedonal or inflammatory).
If the acne is mainly comedonal with minimal inflammation, change to a topical retinoid. Use:
1adapalene 0.1% cream or gel topically, once daily at night for 6 weeks then review1 adapalene adapalene adapalene
OR
1tretinoin 0.025% cream topically, once daily at night for 6 weeks then review1 tretinoin tretinoin tretinoin
OR
1trifarotene 0.005% cream topically, once daily at night for 6 weeks then review12. trifarotene trifarotene trifarotene
Improvement with a topical retinoid should be seen by 6 weeks, and should continue to improve for up to 6 months. For practical and safety advice about using retinoids, see Treatments used for acne.
If the response to the topical retinoid is not adequate after 6 weeks, consider a higher dose of the retinoid (if using tretinoin), or reassess the dominant type of acne present and consider a topical combination (eg benzoyl peroxide and adapalene).
If the acne is mainly comedonal, with some inflammatory papules and pustules, change to a topical combination of benzoyl peroxide and a retinoid. Use:
benzoyl peroxide+adapalene 2.5%+0.1% gel topically, once daily for 6 weeks, then review. benzoyl peroxide + adapalene benzoyl peroxide+adapalene benzoyl peroxide+adapalene
If acne is not improving, but treatment with benzoyl peroxide and adapalene is well tolerated, increase the strength of adapalene. UseDréno, 2018Stein Gold, 2016:
benzoyl peroxide+adapalene 2.5%+0.3% gel topically, once daily for 6 weeks, then review. benzoyl peroxide + adapalene benzoyl peroxide+adapalene benzoyl peroxide+adapalene
If the acne is mainly inflammatory papules and pustules, with some comedones, change to a topical combination of benzoyl peroxide and an antibiotic. Use:
benzoyl peroxide+clindamycin 5%+1% gel topically, once daily for 6 weeks, then review. benzoyl peroxide + clindamycin benzoyl peroxide+clindamycin benzoyl peroxide+clindamycin
Topical clindamycin can be used alone if the patient’s skin is prone to irritation (eg patients with atopic skin conditions).
If the acne is a mix of both comedonal and inflammatory papules and pustules, change to a topical combination of a retinoid and an antibiotic. Use:
tretinoin+clindamycin 0.025%+1% gel topically, once daily at night for 6 weeks, then review. tretinoin + clindamycin tretinoin+clindamycin tretinoin+clindamycin
Topical clindamycin can be used alone if the patient’s skin is prone to irritation (eg patients with atopic skin conditions).
Avoid using topical antibiotic therapy long term. Once papular inflammation has resolved or inflammatory acne activity is controlled, change to a single-ingredient preparation containing a topical retinoid or benzoyl peroxide for maintenance Asai, 2016The Australasian College of Dermatologists, 2021Zaenglein, 2016Zouboulis, 2015. If the inflammation recurs, resume the topical combination containing an antibiotic, and regularly review for ongoing need.
If topical preparations are not sufficiently effective, continue topical therapy and add oral therapy as for moderate to severe acne.
If topical preparations are not tolerated, switch to oral therapy as for moderate to severe acne.
