Pompholyx
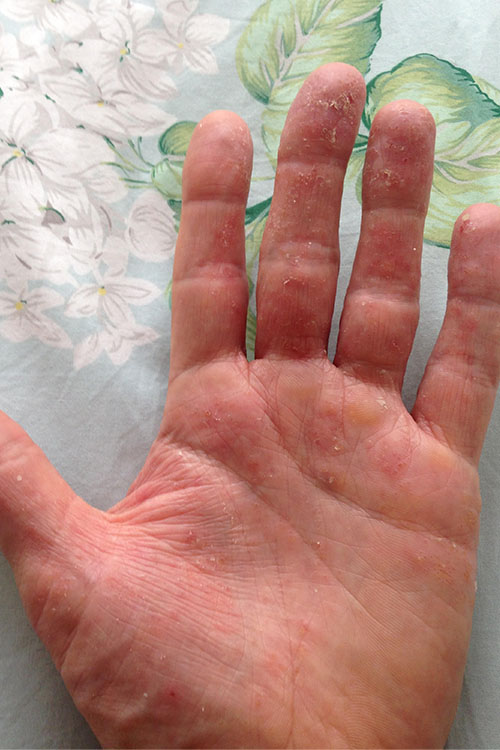
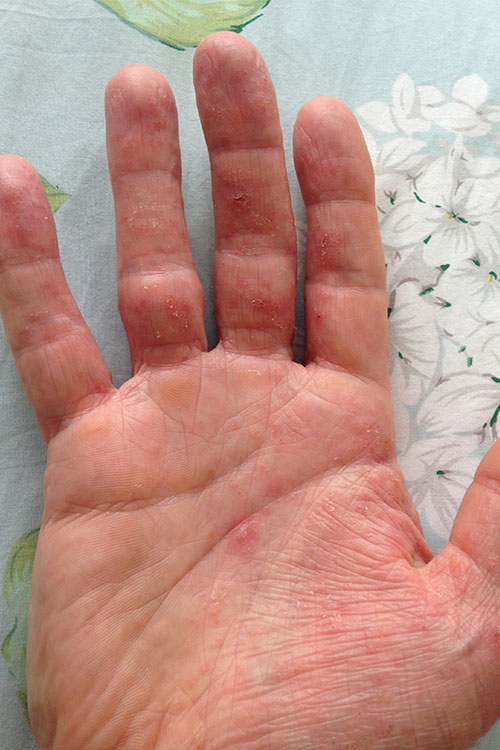
Pompholyx (also called dyshidrotic eczema, vesicular dermatitis, autoeczematisation, or vesicular hand and foot dermatitis) presents as small vesicles (or if severe, as bullae) on the palms, along the fingers, and on the soles. See here for photos of pompholyx. The cause is unclear, but it is associated with atopic dermatitis. Pompholyx can be precipitated by acute inflammatory tinea (eg of the feet) or molluscum contagiosum. Other aggravating factors include overheating, irritants and stress. Exclude scabies infection.
Pompholyx is often difficult to treat, and specialist advice may be required. Early treatment is important for efficacy. The condition usually recurs, and patients are aware of symptoms, such as itching, before small blisters appear.
The initial phase may be exudative as the blisters burst, and itching is often intense. If there are clinical signs of infection, take a bacterial swab for cultures and susceptibility testing. Empirical antibiotics may be started while waiting for results of microbiological testing; see treatment of infection in atopic dermatitis for drug and dose recommendations.
To help dry the affected skin, bathe the hand or foot in salt water (salt 2.5 g [approximately 1/2 (half) teaspoon] dissolved in 250 mL [1 cup] of water). Pat the skin dry, then apply a topical corticosteroid. Use a cream initially, then an ointment when the skin dries up.
For an initial episode of acute pompholyx, use a potent topical corticosteroid:
1betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% cream or ointment topically, once or twice daily until skin is clear, with or without a modified dressing betamethasone dipropionate betamethasone dipropionate betamethasone dipropionate
OR
1betamethasone valerate 0.1% cream or ointment topically, once or twice daily until skin is clear, with or without a modified dressing betamethasone valerate betamethasone valerate betamethasone valerate
OR
1mometasone furoate 0.1% cream or ointment topically, once or twice daily until skin is clear, with or without a modified dressing. mometasone furoate mometasone furoate mometasone furoate
For recurrent episodes of acute pompholyx, apply a more potent topical corticosteroid. Use:
betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% ointment in optimised vehicle topically, once or twice daily until skin is clear or for up to 2 weeks, with or without a modified dressing. betamethasone dipropionate betamethasone dipropionate betamethasone dipropionate
Episodes of severe pompholyx (ie with significant blistering and extreme itch) may need oral corticosteroids. Use:
prednisolone (or prednisone) 15 to 25 mg (child: 0.25 to 0.5 mg/kg up to 25 mg) orally, once daily for 3 to 4 days, then taper over 1 to 2 weeks to minimise rebound flare. prednisolone prednisolone prednisolone
Advise patients on general measures to protect the hands (see Hand contact dermatitis) when the skin is clear.
If the patient does not respond to therapy, refer for specialist advice.