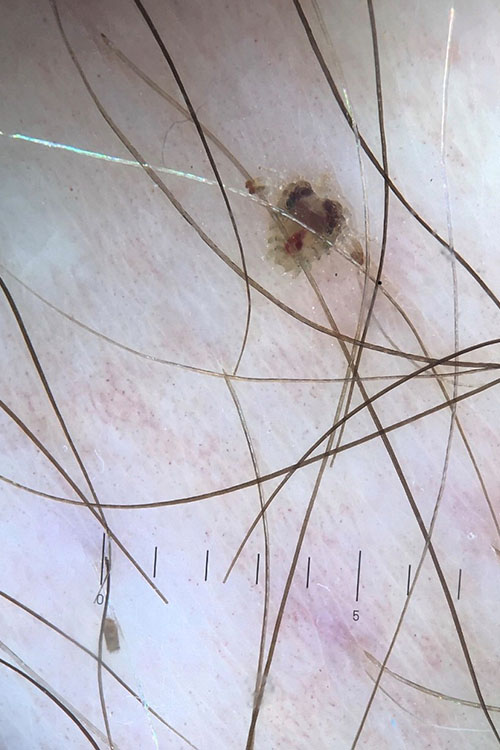
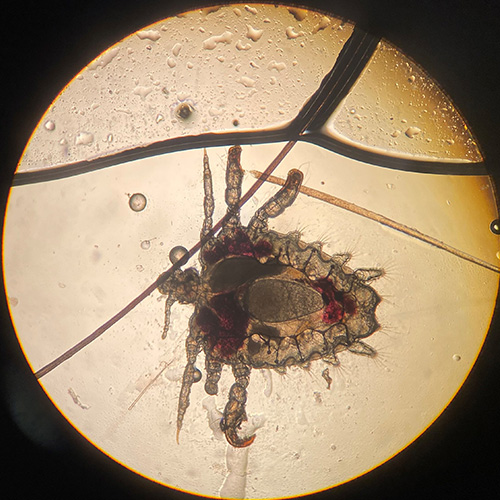
Pubic lice
Pubic lice (Phthirus pubis) colonise pubic, axillary, beard and body hair. Infestation may also involve eyebrows and eyelashes. See here for photos of pubic lice. Itch is the main symptom. Infestation is spread by close physical contact (often sexual contact), and pubic lice are most often seen in adults. Screen for other sexually transmissible infections (STIs) including HIVSalavastru, 2017. Sexually transmissible infections are indicator conditions for HIV testing1. If pubic lice are present on children, consider the possibility of sexual abuse.
Examine the entire body surface for lice, including eyelashes and eyebrows. Treat pubic lice as for head lice. Shaving pubic hair is beneficialVeraldi, 2018. Wash underwear and bedclothes on a hot cycle (60℃), and machine dry. Items that cannot be washed can be dry-cleaned or sealed in plastic bags for 14 daysBetter Health Channel, 2020Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019.
If the eyelashes are infested with lice, apply a thick layer of white soft paraffin to the eyelashes twice a day for 8 days to suffocate the lice. Eggs may be removed with fine forceps; however, this may be difficult because slit lamp control is required. Refer to an ophthalmologist if needed.
Treatment failure may be due to re-infection; household members and sexual partners in the previous 3 monthsSalavastru, 2017 must be examined and treated if necessary.