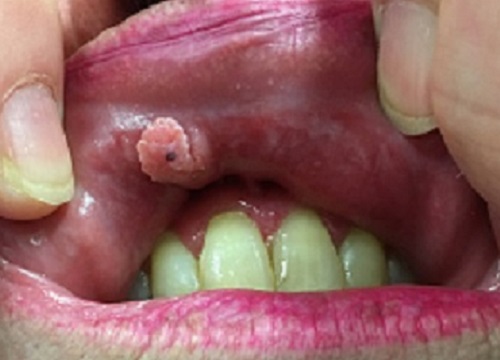
Human papillomavirus–related oral lesions
Human papillomaviruses (HPV) can cause a wide range of oral mucosal lesions. The virus is usually transmitted by direct contact with a lesion.
Squamous papilloma is the most common oral HPV lesion, appearing as a protruding growth with small finger-like projections (see Papilloma of the right maxillary labial mucosa). Sexually transmitted HPV infections can cause oral HPV lesions called condyloma acuminata. Verruca vulgaris—the common wart—is also caused by HPV infection and may present in the oral cavity. Both condyloma acuminata and verruca vulgaris can be clinically similar to squamous papilloma.
Oncogenic types of HPV are now recognised as a cause of some squamous cell carcinoma, particularly of the posterior tongue, tonsillar region and oropharynx. These appear to be a distinct entity, separate to the oral cancers associated with alcohol and tobacco use.
Refer patients with suspected HPV lesions to an appropriate specialist for biopsy and management1