Dental anatomy and terminology
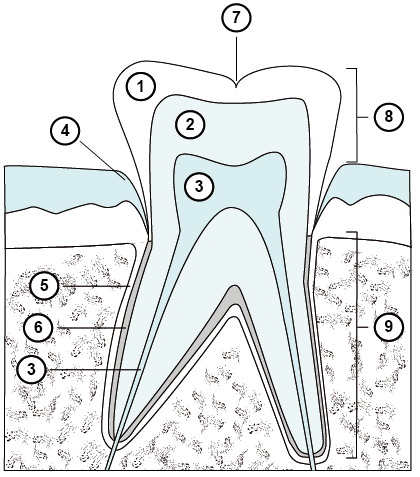
1. Enamel: The hard, calcified substance that is the surface of a crown of a tooth.
2. Dentine: The calcified tissue that forms the major part of a tooth. In the crown of the tooth, the dentine is covered by enamel. The pulp chamber of the tooth is enclosed by dentine.
3. Pulp: The organ at the centre of a tooth containing blood vessels, connective and neural tissue, and cells that produce dentine. Blood vessels and neural tissue enter the tooth from the apex of the root.
4. Gingiva: The marginal part of the gum that surrounds the tooth where it emerges from the deeper, supporting tissues.
5. Periodontal ligament: The ligament that connects a tooth, by its root, to the supporting bone.
6. Cementum: The calcified tissue on the surface of the root of a tooth, which provides attachment for the periodontal ligament.
7. Fissure: A naturally occurring crevice in the enamel.
8. Crown: The part of the tooth that is visible and is above the gingival margin.
9. Root: The part of the tooth below the gingival margin; it is connected through cementum on its surface and the fibres of the periodontal ligament to the supporting bone.
