Preprocedural risk assessment
[NB1] [NB2]
Assess the patient’s age, and medical and surgical history:
age—procedural sedation and analgesia should only be administered to children younger than 2 years by specialists with expertise in managing airway compromise in this age group
current medications—concomitant use of sedatives increases the risk of complications from procedural sedation and analgesia
hypersensitivities—do not use a drug or excipient to which the patient is hypersensitive
comorbidities
- children aged 2 to 5 years have a high risk of procedural complications if they have:
- a current or recent upper respiratory tract infection
- history of asthma
- history of obstructive sleep apnoea
- ASA score of 3 or more
- adults and children older than 5 years are at a high risk of procedural complications if they have an ASA score of 3 or more.
- ASA 3—severe systemic disease (eg obesity, poorly controlled diabetes, hypertension)
- ASA 4—severe systemic disease that is an ongoing threat to the patient’s life (eg cardiovascular event within the past 3 months, severely reduced ejection fraction, end-stage kidney disease)
- ASA 5—a moribund patient not expected to survive without an operation (eg massive trauma, multiple organ/system dysfunction)
predictors of difficult bag–mask ventilation—difficult bag–mask ventilation is likely in patients with any of the following characteristics:
- a bushy beard
- a history of snoring or obstructive sleep apnoea
- damaged/loose teeth or dentures
- obesity [NB3]
predictors of difficult intubation—intubation is likely to be difficult in patients with any of the following characteristics:
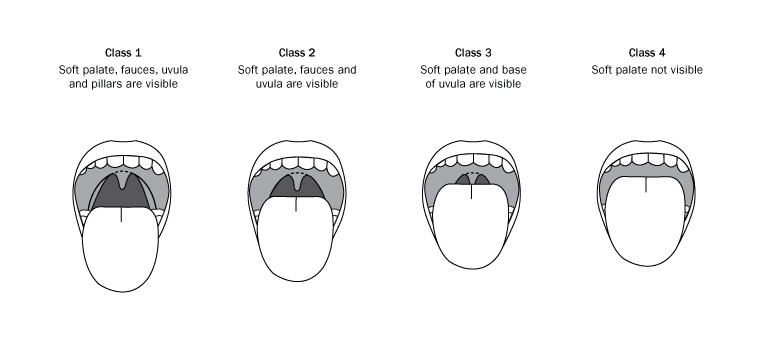
- a Mallampati score of 3 or 4; see Modified Mallampati classification
- an inability to open their mouth more than 4 cm
- limited neck movement
- difficulty in protruding their lower jaw
- a history of difficult intubation
ASA = American Society of Anaesthesiologists
NB1: Patients identified as being at high risk should have specialist input or review, or have the procedure deferred.
NB2: Procedural sedation and analgesia in children younger than 2 years requires specialist skills (eg a senior or paediatric emergency physician, senior paediatrician or anaesthetist) and is not within the scope of these guidelines.
NB3: Do not use adult body mass index (BMI) values for children. For an online BMI calculator for children, see the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.