Arterial blood gas analysis
Arterial blood gas analysis is used to assess blood oxygenation, acid–base balance and adequacy of ventilation. It provides:
- partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2)
- partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2)
- pH
- calculated values for bicarbonate concentration and base excess.
Arterial blood gas analysis is useful for:
- guiding management of severe acute respiratory disorders in hospital
- assessment of disorders associated with chronic respiratory failure
- assessment for long-term domiciliary oxygen therapy.
Normal values for the parameters measured in arterial blood gas analysis are given in Normal values for arterial blood gas analysis.
|
Parameter |
Normal value |
|---|---|
|
pH |
7.35 to 7.45 |
|
PaO2 |
80 to 100 mmHg [NB1] |
|
PaCO2 |
35 to 45 mmHg |
|
Bicarbonate concentration |
22 to 26 mmol/L |
|
Base excess |
–2 to +2 mmol/L |
Note:
PaCO2 = partial pressure of carbon dioxide; PaO2 = partial pressure of oxygen NB1: Values depend on age and altitude. | |
[NB1]
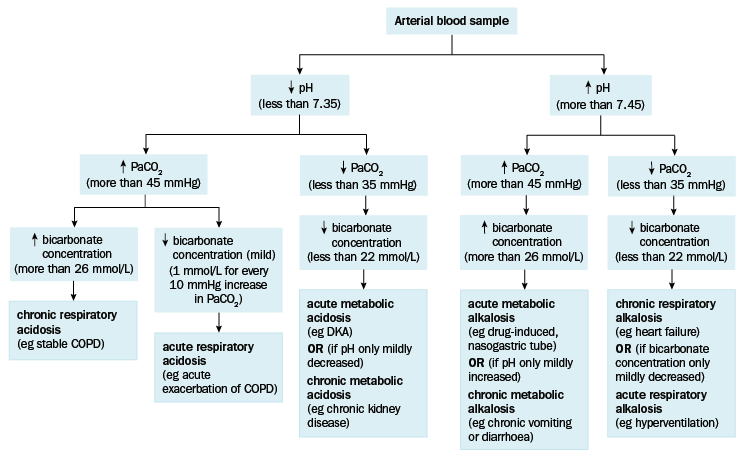
COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DKA = diabetic ketoacidosis; PaCO2 = partial pressure of carbon dioxide
NB1: Interpretation of arterial blood gas results can be complex—seek specialist advice if there is any doubt about the interpretation. The patient’s clinical features should be considered when interpreting arterial blood gas results. Results change as the body compensates for the underlying problem. Results may be influenced by factors relating to sampling technique (eg air bubbles in the specimen), specimen processing (eg delayed processing), and environment (eg body temperature).
