Diagnosis and management of itch without rash
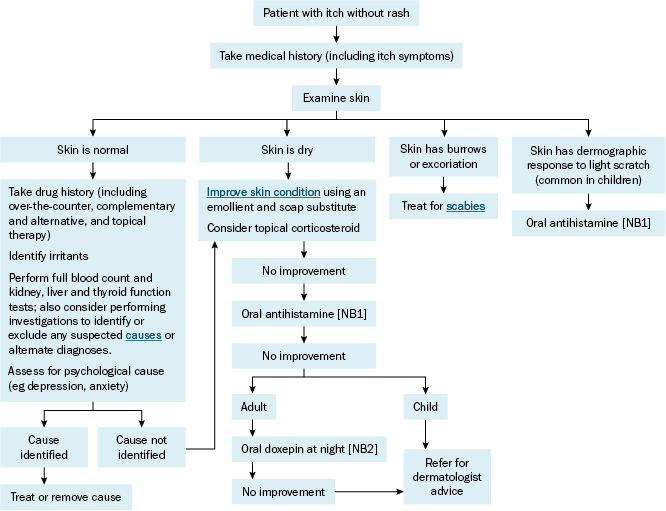
NB1: Less-sedating antihistamines and sedating antihistamines (for sleep disturbance associated with itch) can be used; for doses of oral antihistamines, see Treatment of urticaria.
NB2: Avoid concurrent use of doxepin and a sedating antihistamine because this may result in increased adverse effects (eg sedation, anticholinergic effects).
For itch without rash that has a definite cause (see Causes of itch without rash for causes), the itch typically resolves when the cause is treated or removed (eg treating dry skin, treating scabies, removing irritants). Itch can be an adverse effect of almost any drug; if no other cause is identified, a trial of stopping or changing a drug can be useful to exclude it as the cause.
Itch without rash caused by nerve compression or neuropathy can be treated with appropriate treatments to relieve nerve entrapment.
Itch without rash in children is often caused by dermographism; initial therapy is an oral antihistamine. Less-sedating antihistamines and sedating antihistamines (for sleep disturbance associated with itch) can be used; for doses of oral antihistamines, see Treatment of urticaria.
If the cause of the itch is dry skin or is not known, improve the skin condition by using a soap substitute and applying an emollient. In addition, general measures such as cooling the skin (eg with a cool bath, storing emollients in the fridge before use, using an emollient containing menthol) can reduce itchAndrade, 2020Nowak, 2017.
If required, a topical corticosteroid can be used. For itch without rash on the trunk or limbs, use:
1betamethasone valerate 0.02% cream topically, twice daily for 2 weeks betamethasone valerate betamethasone valerate betamethasone valerate
OR
1triamcinolone acetonide 0.02% ointment topically, twice daily for 2 weeks. triamcinolone acetonide triamcinolone acetonide triamcinolone acetonide
For itch without rash on the face, use:
hydrocortisone 1% cream topically, twice daily for 2 weeks. hydrocortisone hydrocortisone hydrocortisone
If itch persists despite improving the skin condition and topical corticosteroid therapy, trial an oral antihistamine. Less-sedating antihistamines and sedating antihistamines (for sleep disturbance associated with itch) can be used; for doses of oral antihistamines, see Treatment of urticaria.
If itch still persists in an adult, consider adding:
Avoid concurrent use of doxepin and a sedating antihistamine because this may result in increased adverse effects (eg anticholinergic effects, sedation).
If these treatments are not successful, refer the patient for dermatologist advice and specialist treatments (eg ultraviolet B phototherapy)Andrade, 2020Nowak, 2017. While waiting for referral, consider performing investigations to identify or exclude any suspected causes (see Causes of itch without rash) or alternate diagnoses of itch without rash.
